Diamond Grading :
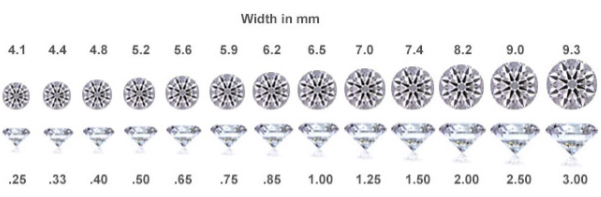
Carats
The Carat is the measure of the actual weight of the diamond. A carat is divided into 100 points. A 0.50 carat diamond may also be referred to as 50 points.
Stones that have too high a depth percentage carry more weight in the height of the diamond where it does not add to the visual size appearance.
Color
Diamond color is all about what you can't see. Lesser the color, higher their value. On the basis of color, diamonds are allocated a grade, starting with D, representing colorless, and continue with increasing presence of the color to the letter Z.

CUT & POLISH & SYMMETRY
CUT
The cut is the most important element which reflects its brilliance, sparkle, fire and scintillation, which is mostly determined by 3 factors, proportion, polish & symmetry. Each diamond is assigned an overall cut grade from Excellent to Poor.
POLISH
All facets of a diamond are carefully polished to eliminate all imperfections, characteristics such as abrasions, scratches, nicks and polishing marks on the surface of the diamond to give the mirror shine and the final beauty
EX- Excellent GD- Good VG- Very Good
SYMMETRY
Symmetry is the balance and regularity / evenness of facets, Facets are compared in opposing pairs, defined as following:
EX- Excellent GD- Good VG- Very Good
Type Of Fluorescence
Fluorescence, the effect ultraviolet (UV) light has on a diamond, is an important consideration when selecting a diamond. When UV light strikes a diamond with fluorescent properties, the stone emits a glow that is usually blue, but can also reflect shades of green, yellow, white, pink, orange, and red. The sources of fluorescence, boron and nitrogen, are the same mineral properties that lend color to a diamond. Fluorescence can occur in different intensities. Gemological laboratories rate the fluorescence of each diamond on a scale from "None" to "Very Strong"
Learn more

